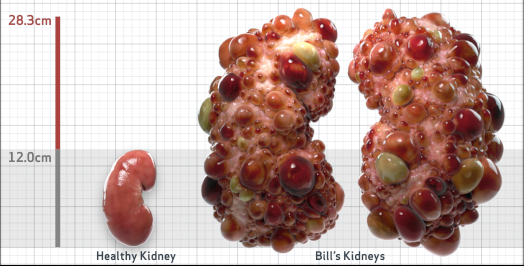
Bill
Bill is 35 years old and has been diagnosed with ADPKD by a kidney ultrasound. Bill is at risk for rapid disease progression, as indicated by the following risk factors: being male, hypertension before age 35, urologic events before age 35, truncating PKD1 mutation, and TKV greater than expected for age. Let's take a closer look with some prognostic tools to confirm the risk of rapid disease progression and assess how rapidly his disease may progress.1,2
- Age35
- Height5'11"
- Weight171 lbs
- SexM
- Race (AA/O)AA
Baseline Assessment3-7
- Serum creatinine (mg/dL)1.15
- eGFR (mL/min/1.73m2)82
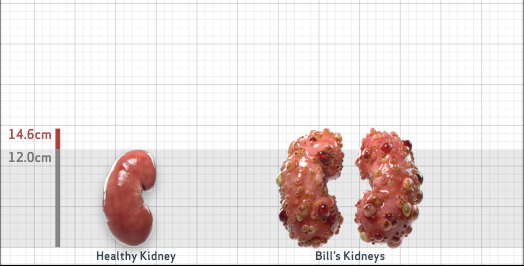
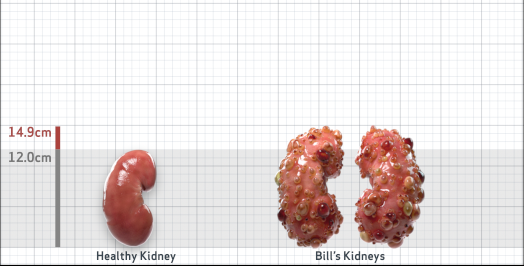
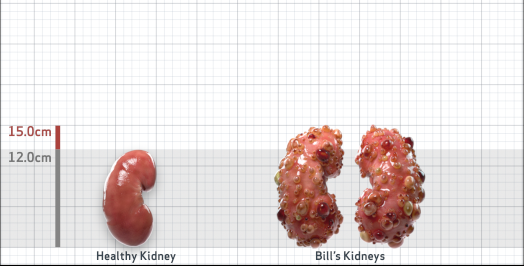
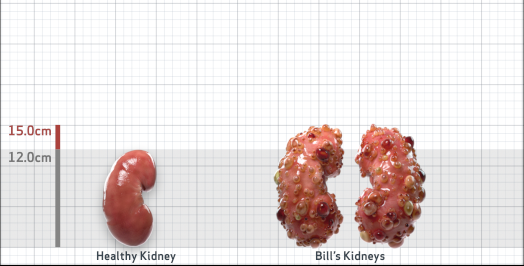
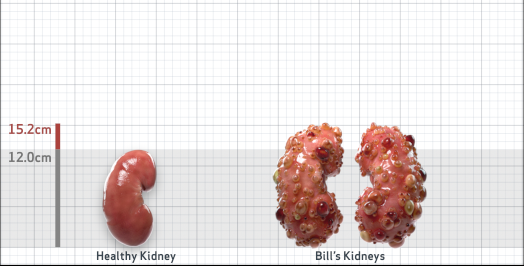
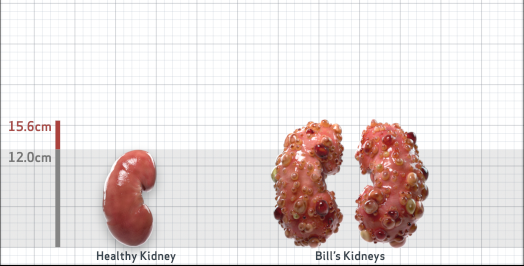
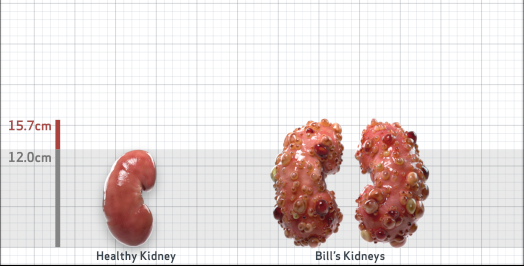
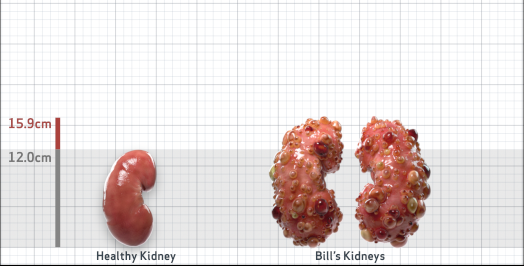
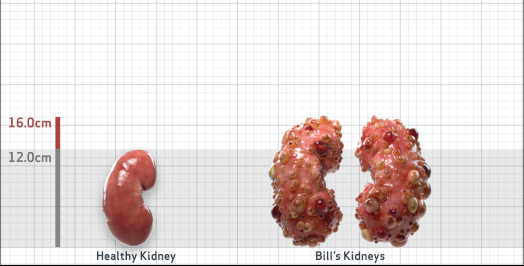
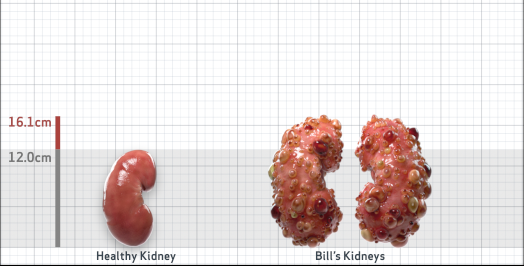
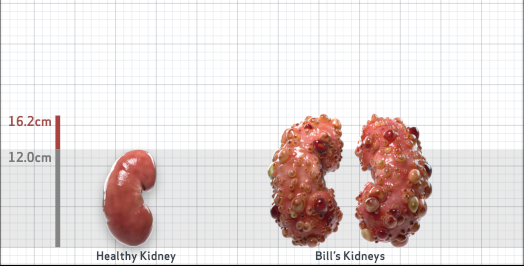
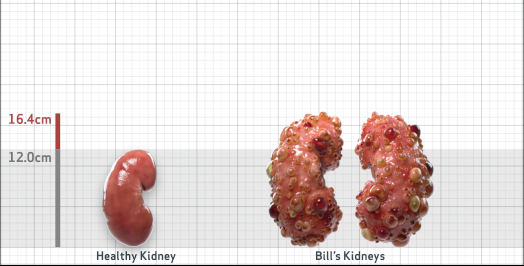
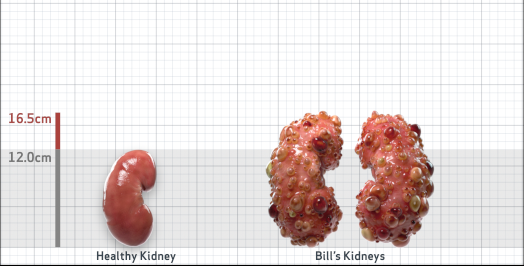
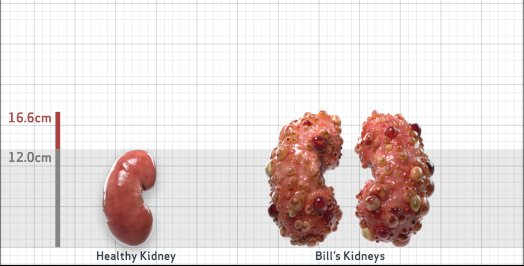
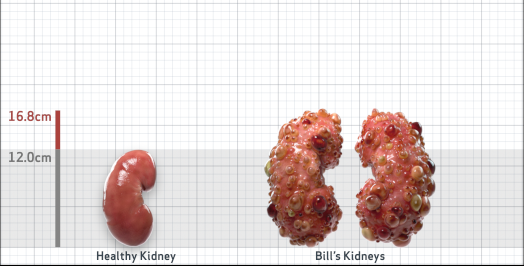
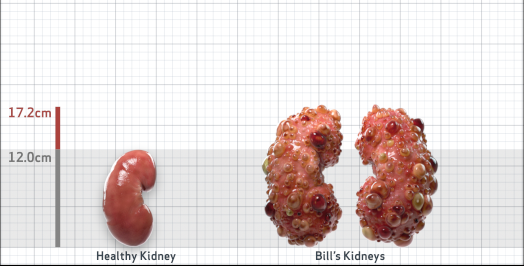
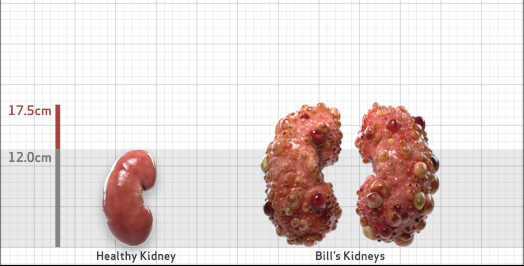
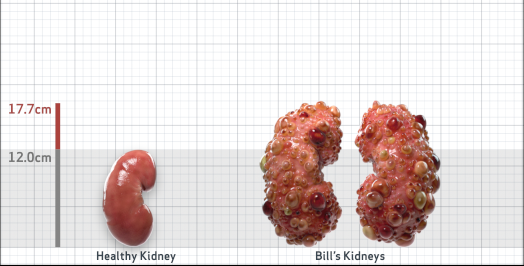
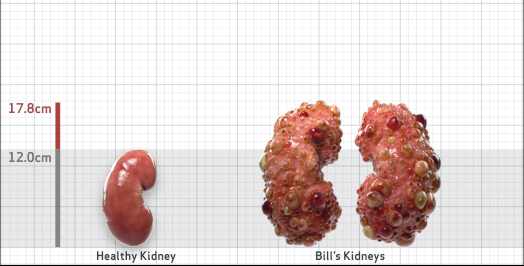
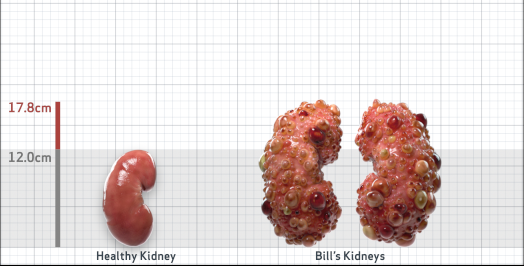
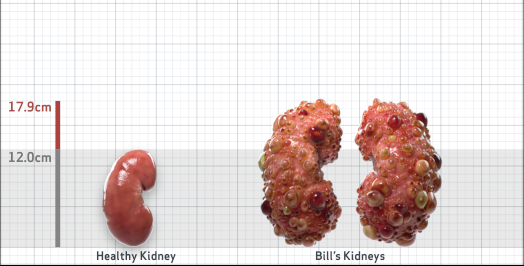
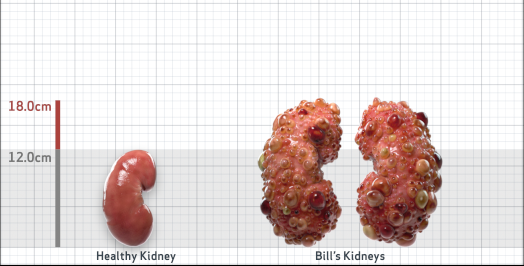
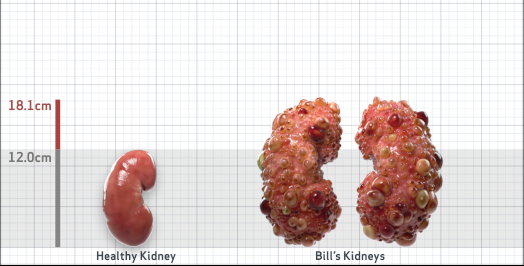
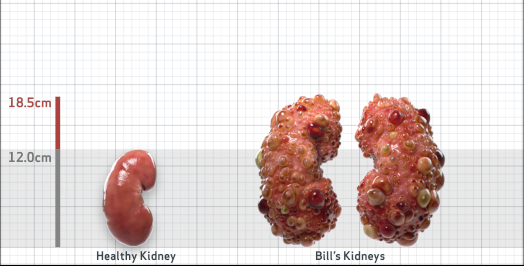
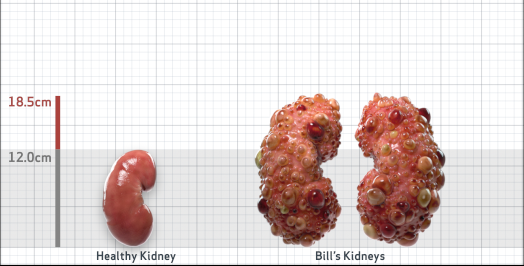
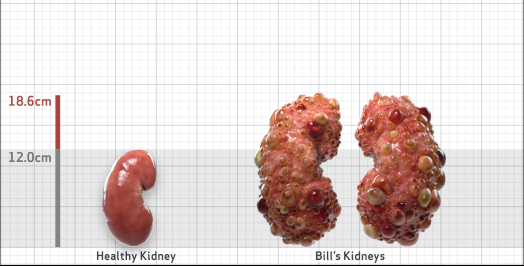
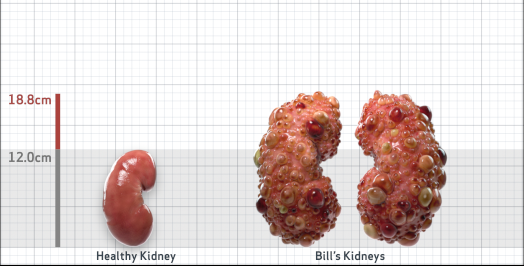
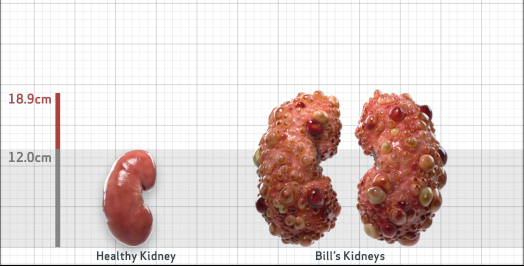
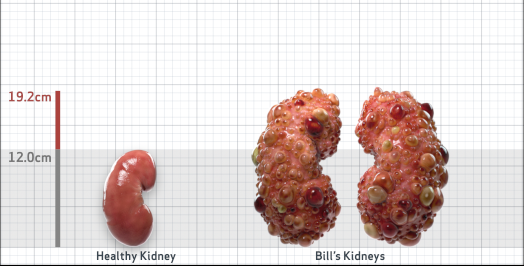
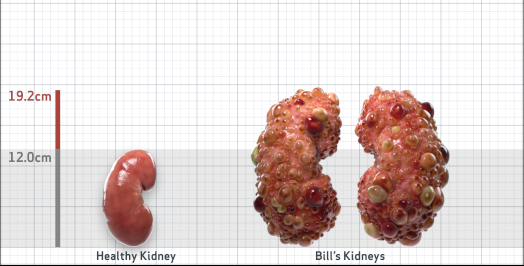
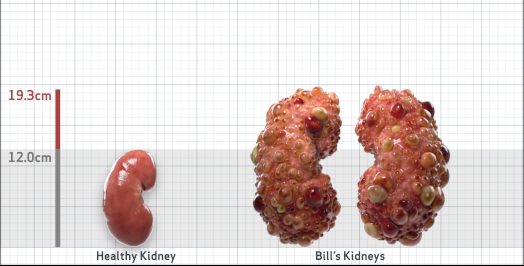
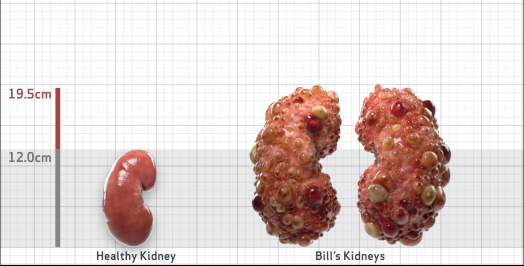
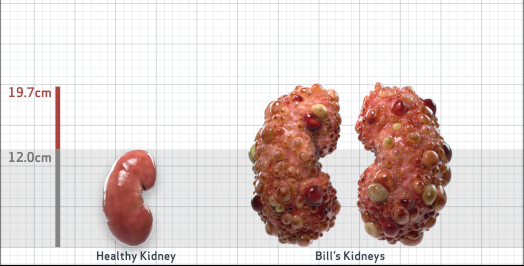
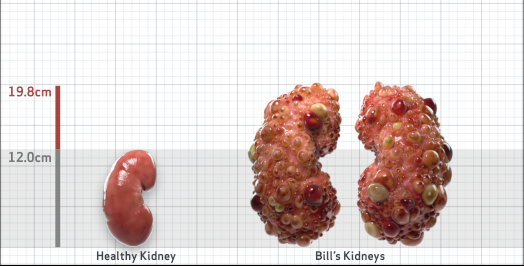
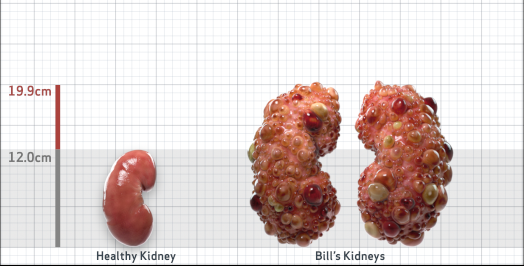
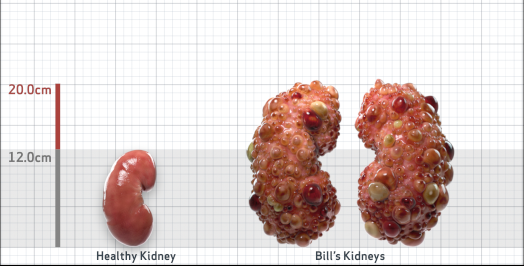
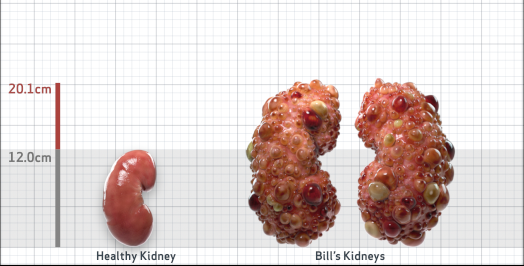
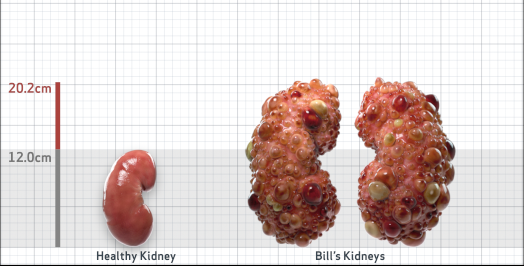
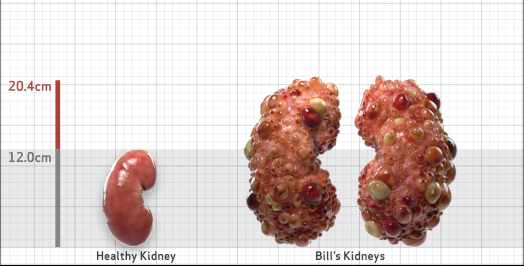
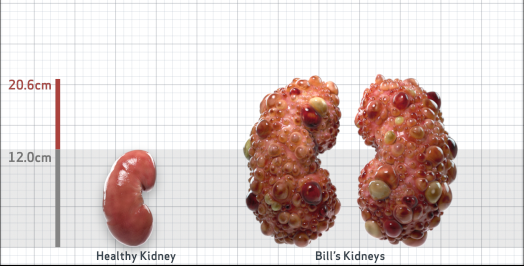
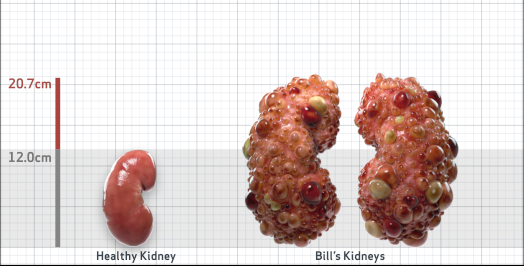
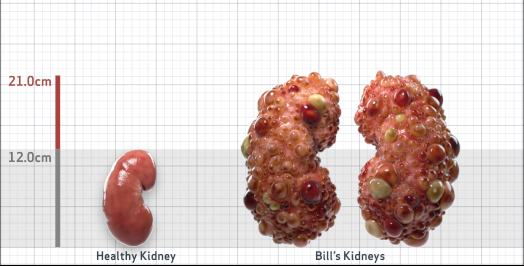
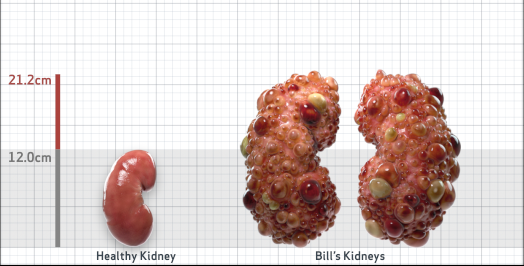
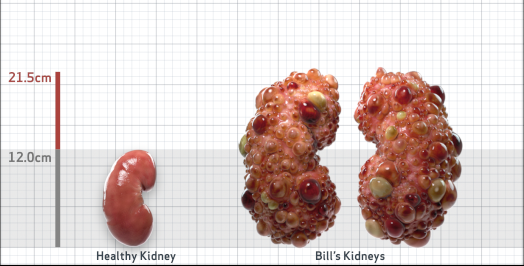
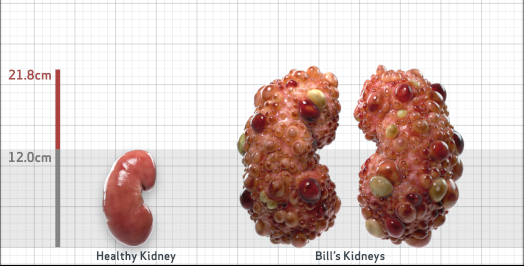
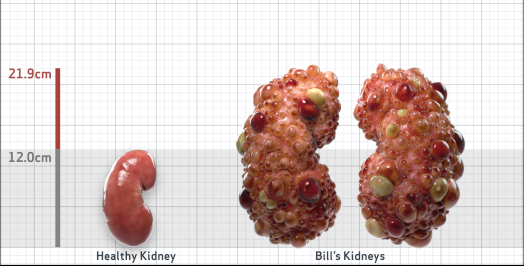
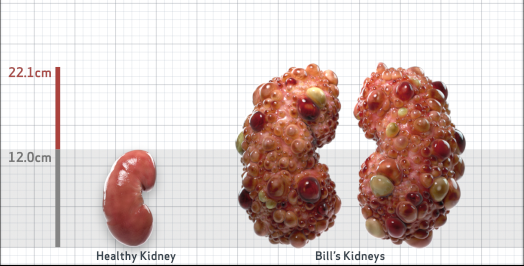
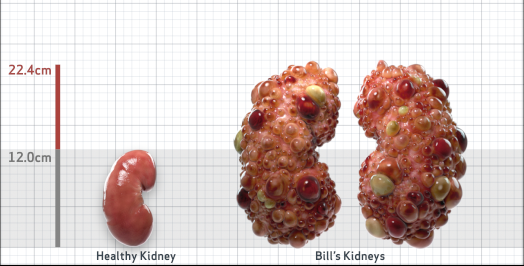
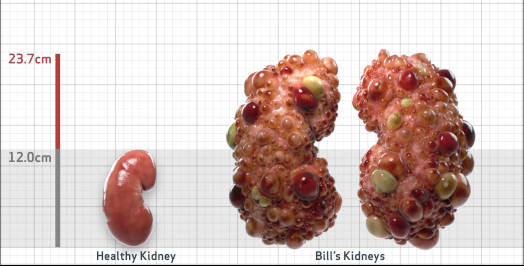
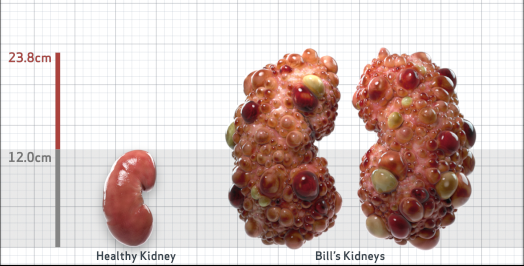
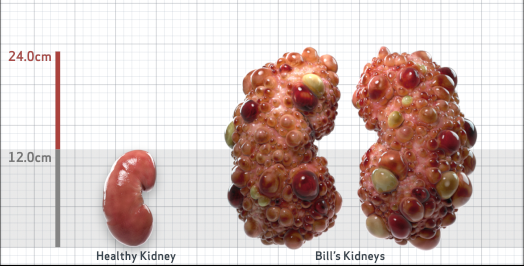
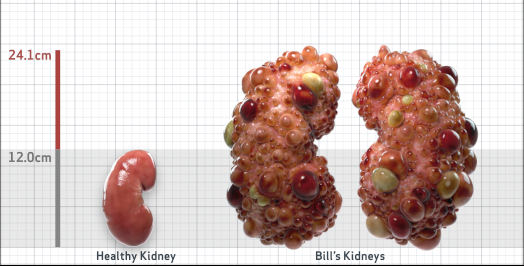
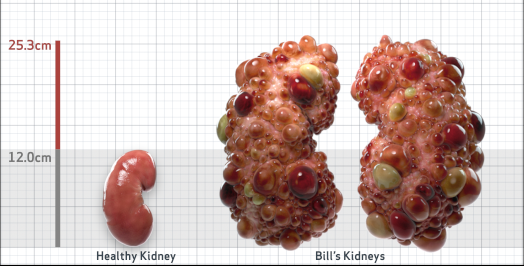
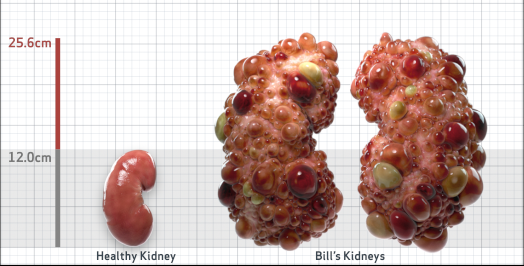
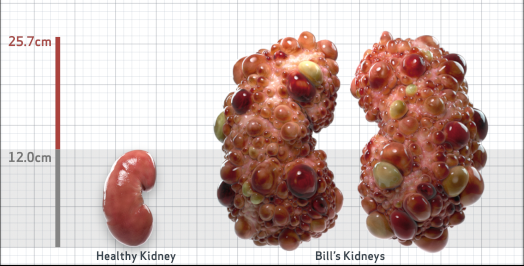
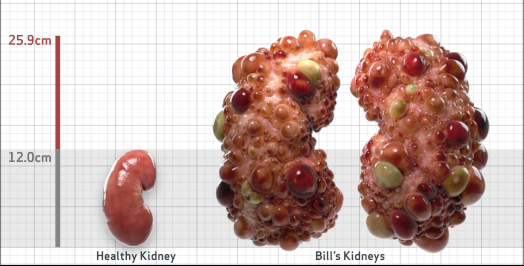
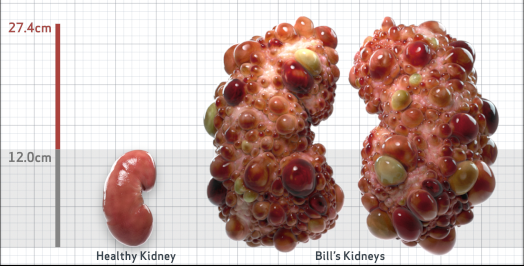
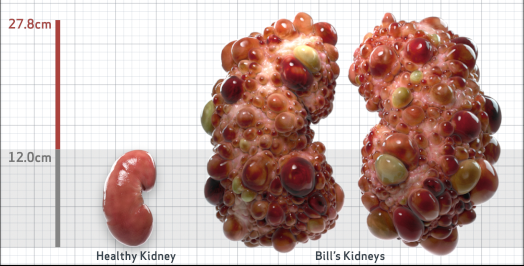
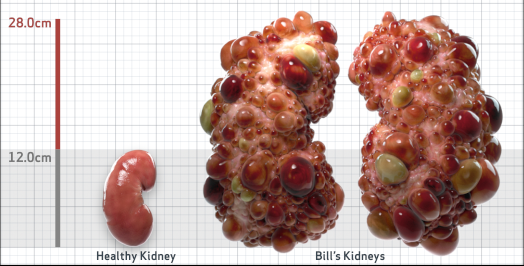
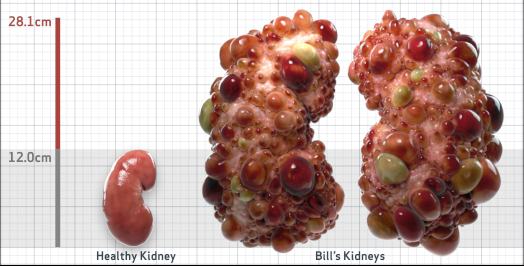
- Ultrasound kidney length (cm)Not obtained
- Hypertension before 35?Yes
- Urological event before 35?Yes
- Family members with ESKD?No
- MutationsTruncating PKD1
- PROPKD Score9 - HIGH risk of progression to ESKD
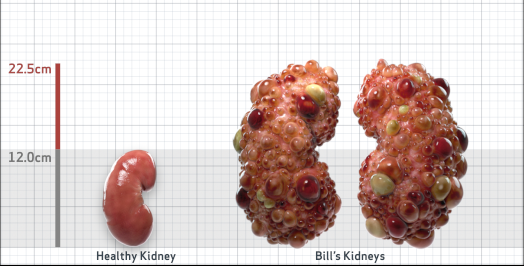
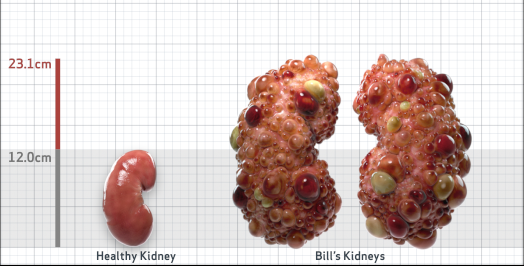
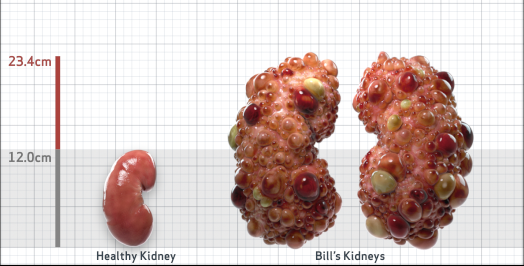
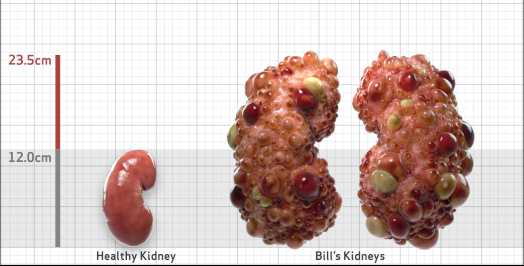
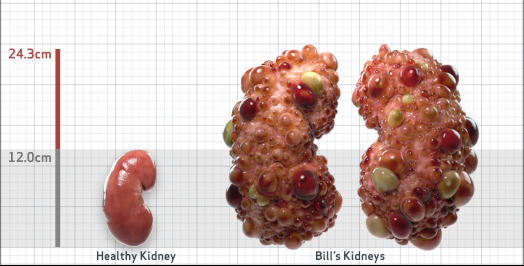
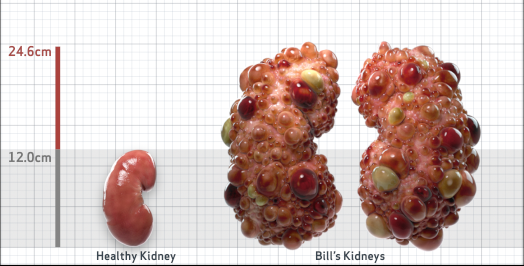
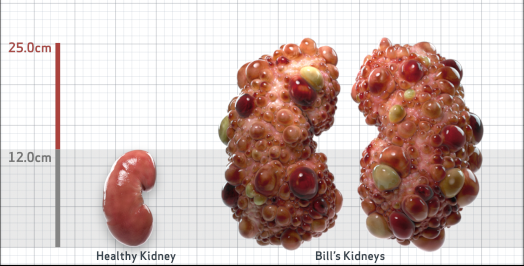
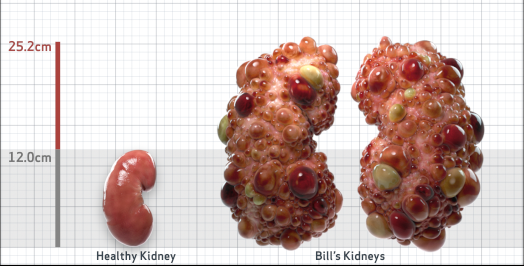
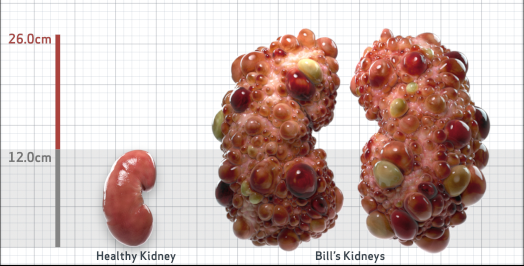
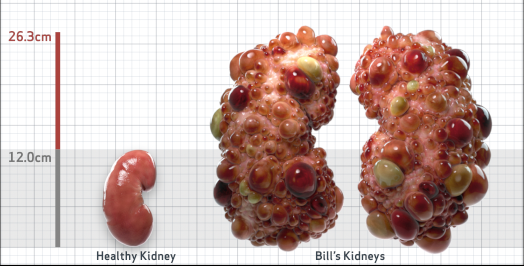
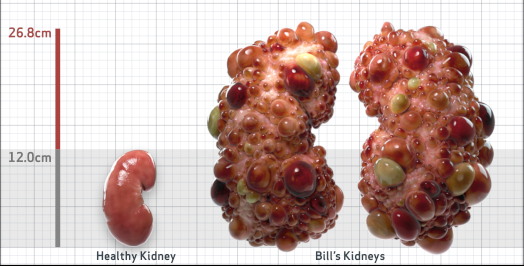
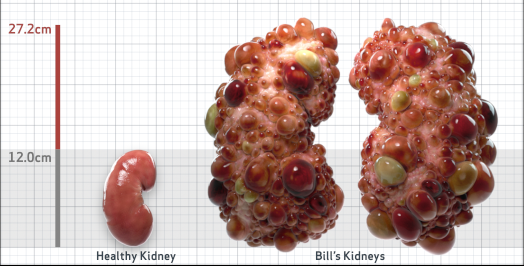
- htTKV (mL/m)1,343
- Other risk factorsNone
- ADPKD Imaging Classification
Class 1E: High Risk for eGFR decline
>6% estimated yearly percentage increase in kidney growth
ESTIMATED AGE AT ESKD47
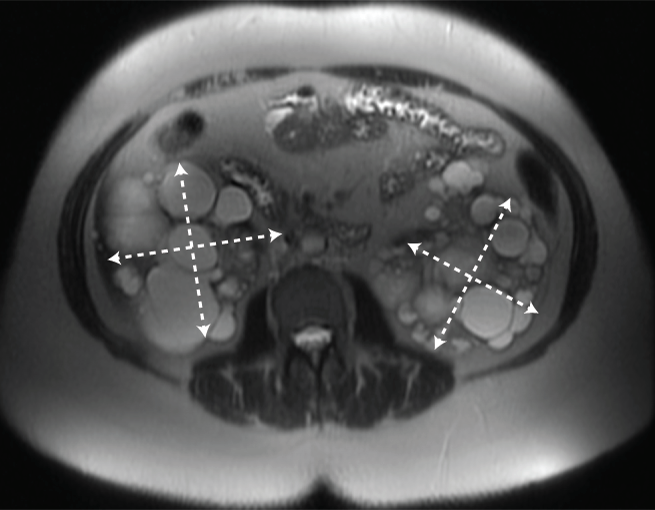
MRI/CT SCANS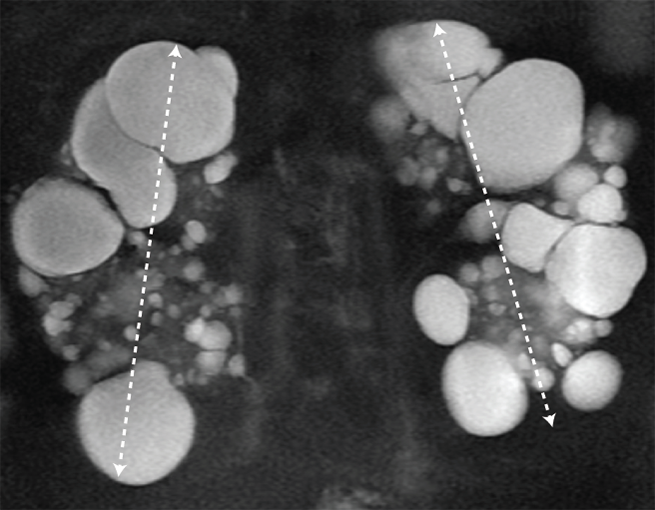
Disease Progression2-5,7-10


Click on the flags below to walk through an assessment that confirms rapid disease progression risk and assesses how rapidly Bill’s disease may progress
Schrier RW, et al. Predictors of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease progression. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014;25:2399-2418.
Gansevoort RT, et al. Recommendations for the use of tolvaptan in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: a position statement on behalf of the ERA-EDTA Working Groups on Inherited Kidney Disorders and European Renal Best Practice. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2016;31(3):337-48.
Wetzels JFM, et al. Age- and gender-specific reference values of estimated GFR in caucasians: the Nijmegen biomedical study. Kidney Int. 2007;72:632-637.
Irazabal MV, et al. Imaging classification of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: a simple model for selecting patients for clinical trials. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015;26:160-172.
Imaging classification of ADPKD: a simple model for selecting patients for clinical trials. http://www.mayo.edu/research/documents/pkd-center-adpkd-classification/doc-20094754. Accessed January 09, 2019.
Cornec-Le Gall E, et al. The PROPKD score: a new algorithm to predict renal survival in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;27(3):942-951.
Cheong B, et al. Normal values for renal length and volume as measured by magnetic resonance imaging. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;2:38-45.
Levey AS, et al. Definition and classification of chronic kidney disease: a position statement from kidney disease: improving global outcomes (KDIGO). Kidney Int. 2005;67:2089-2100.
PKD Charity. Fast Facts about ADPKD. The Polycystic Kidney Disease Charity. 2017. https://pkdcharity.org.uk/about-adpkd/just-diagnosed/fast-facts-about-adpkd Accessed January 09, 2019.
Rangan GK, et al. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: a path forward. Semin Nephrol. 2015;35(6):524-537.