Marcus
Marcus is an active 35-year-old and has been diagnosed with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD). He has high blood pressure, but it is well-controlled with medication. PKD has affected Marcus' daily life as he has suffered from lower back and side pain for the past 10 years. Marcus has also had a cyst infection and a few episodes of blood in the urine. Marcus does not have a family history of kidney disease and he is very anxious about what his future holds.
Let’s take a closer look at some tests Marcus' kidney doctor has ordered to better understand how quickly Marcus might progress to kidney failure1,2.
- Age35
- Height5'11"
- Weight171 lbs
- SexM
- Race (AA/O)AA
Lab Tests
| Standard Range | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Serum Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.15 | 0.50 - 1.20 | |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73m²) | 97 | ≥ 60 | |
| Blood Pressure (mmHg) | 130/80 (High, Controlled with Medication) | < 120/80 | |
| Blood in Urine | Yes | ||
| Pain | Yes | ||
| Family History | No |
Imaging Tests
| Standard Range | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| MRI Ordered? | Yes | ||
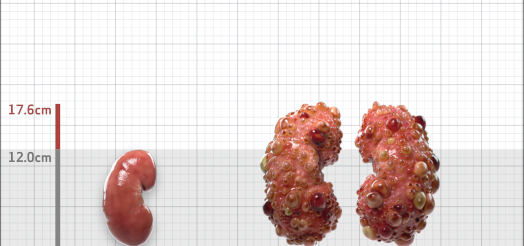
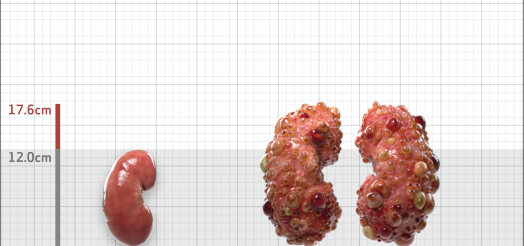
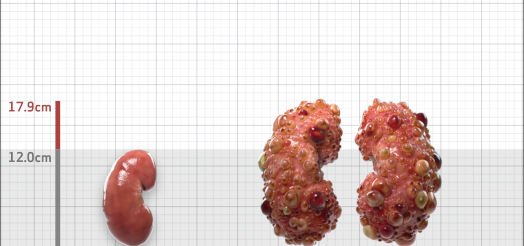
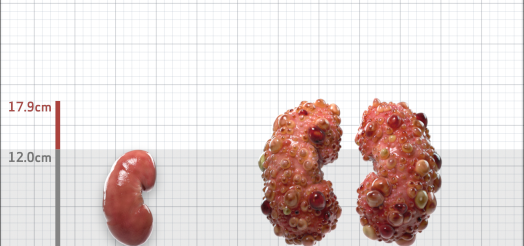
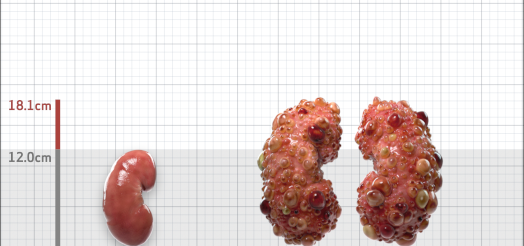
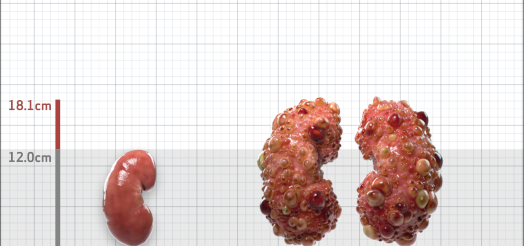
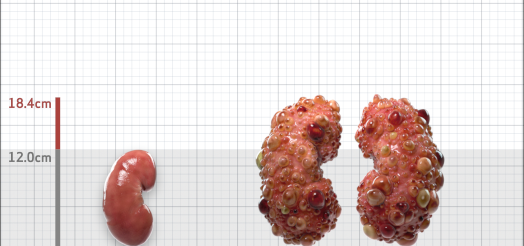
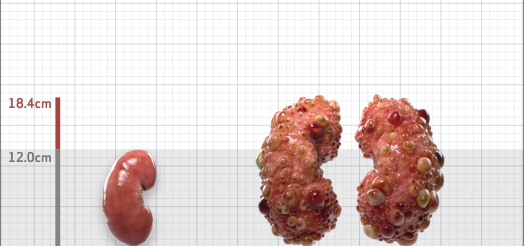
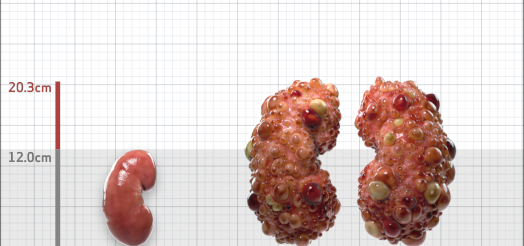
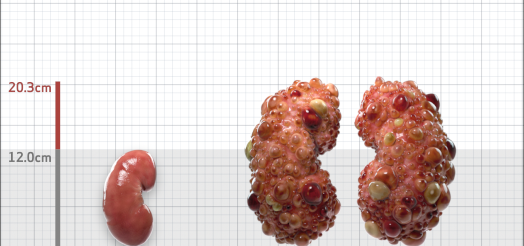
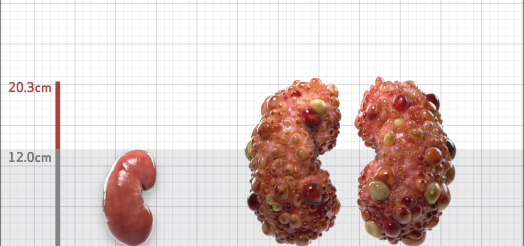
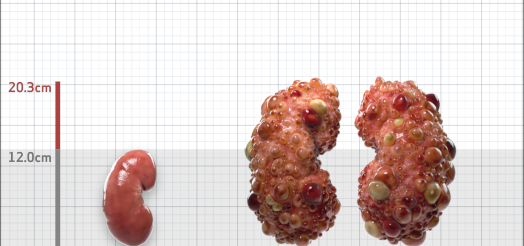
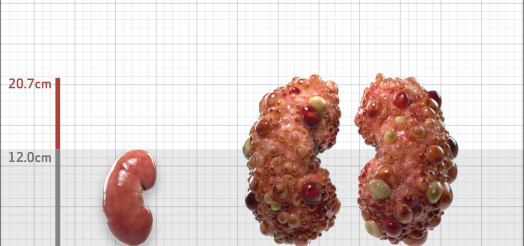
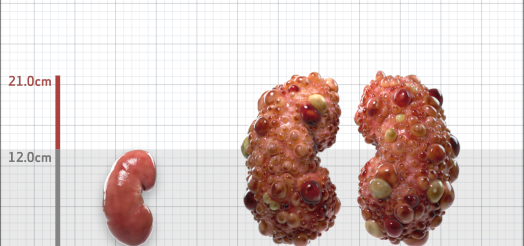
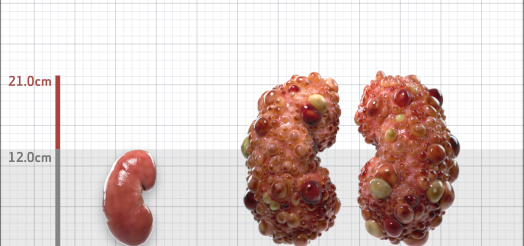
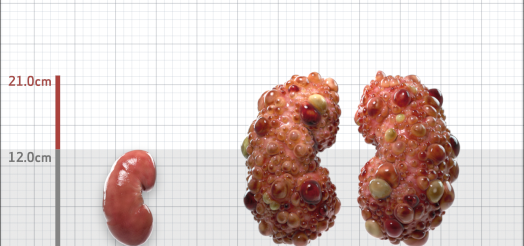
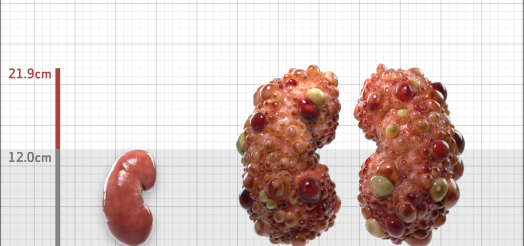
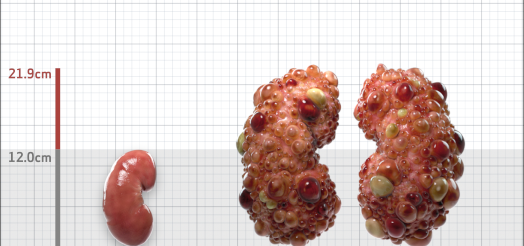
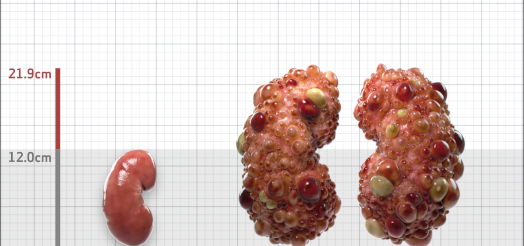
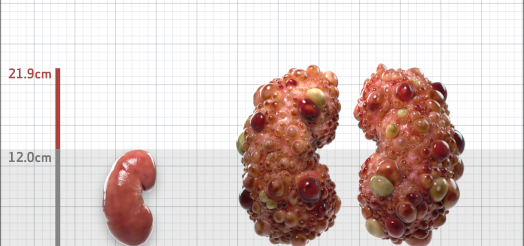
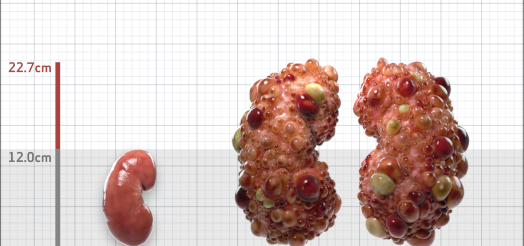
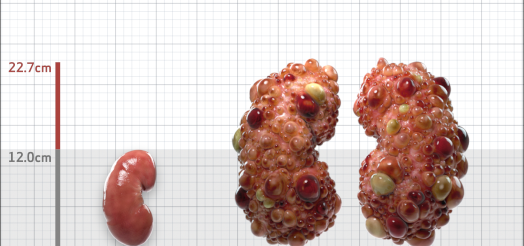
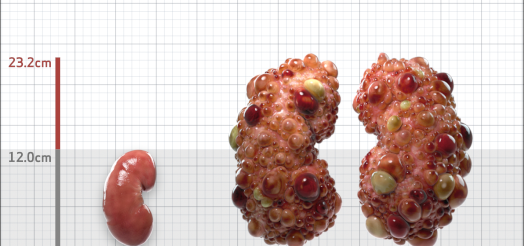
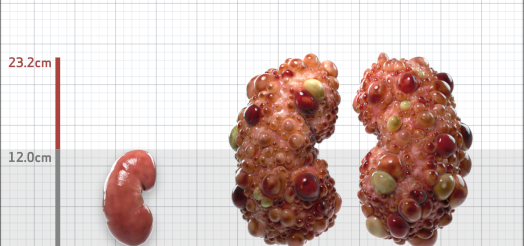
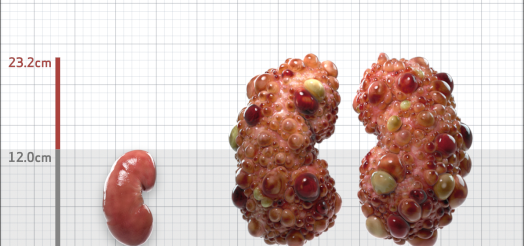
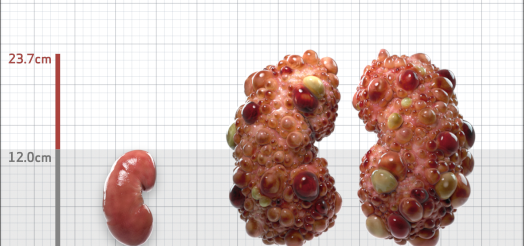
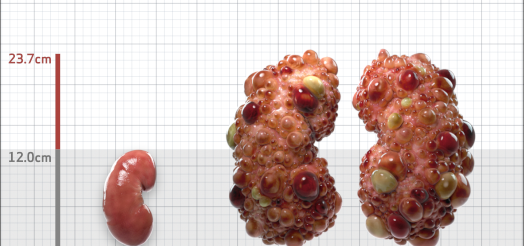
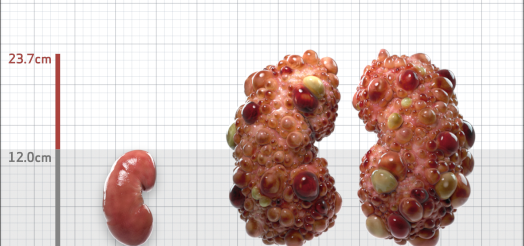
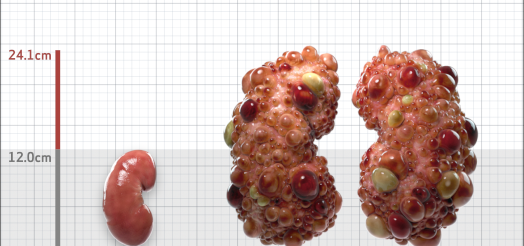
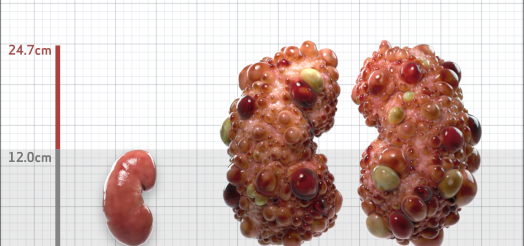
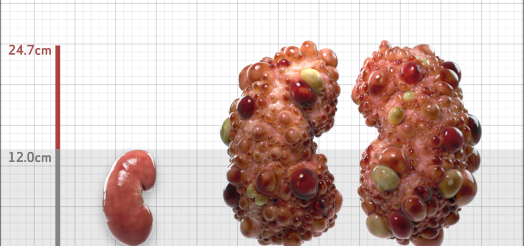
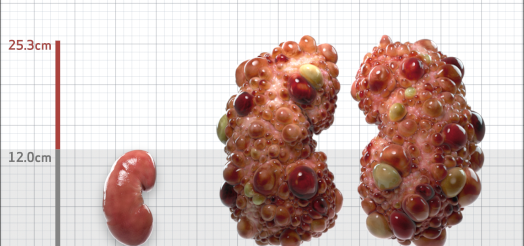
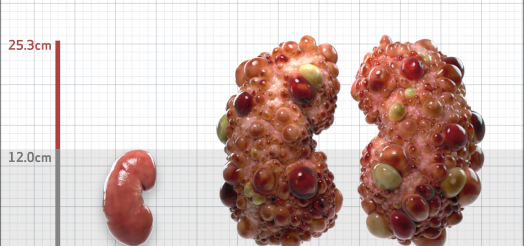
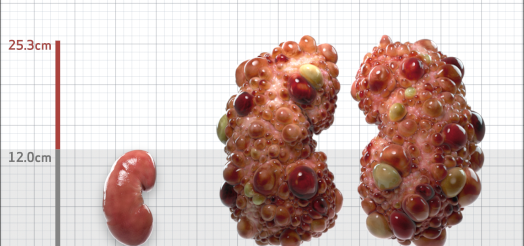
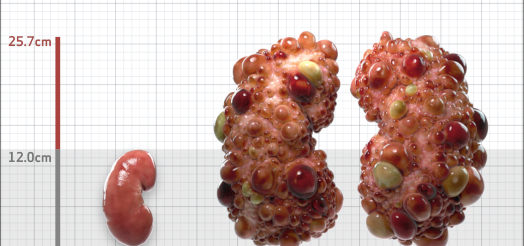
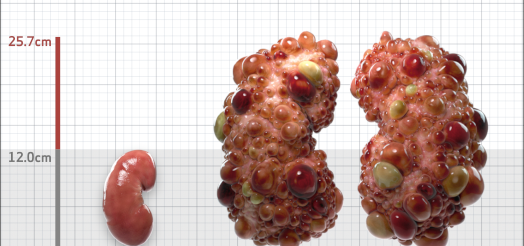
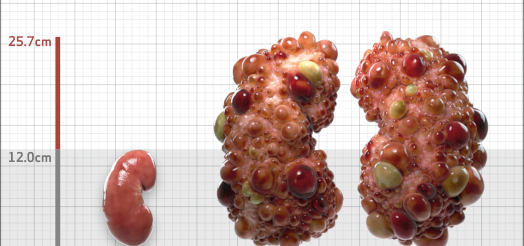
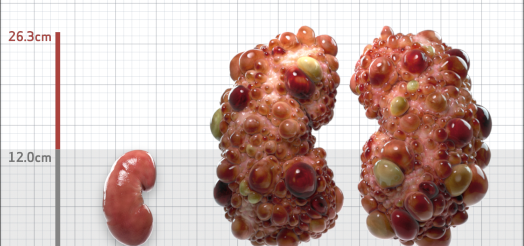
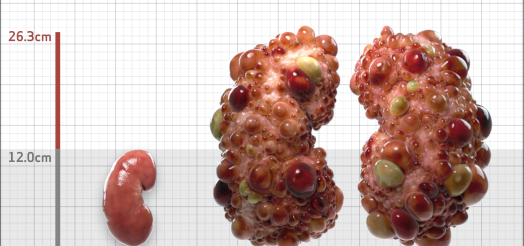
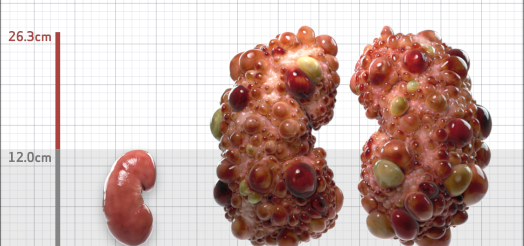
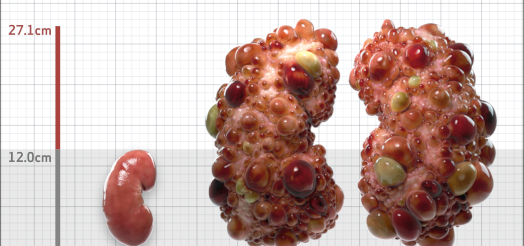
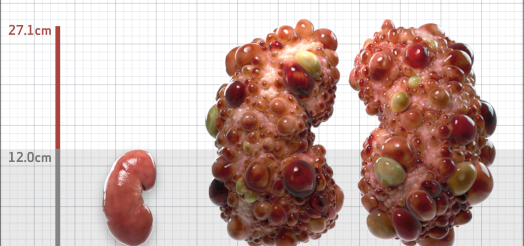
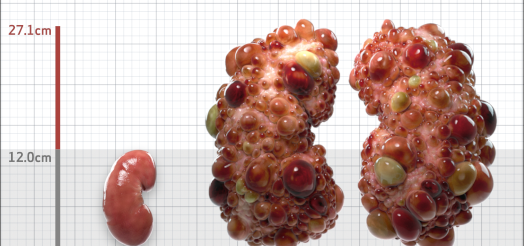
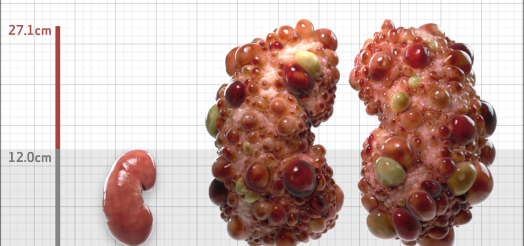
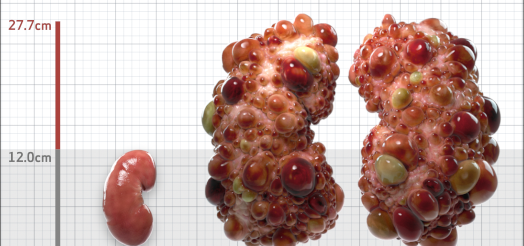
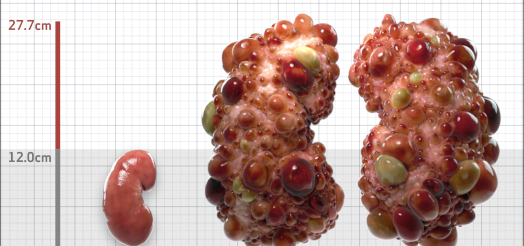
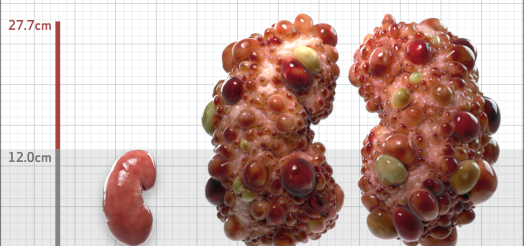
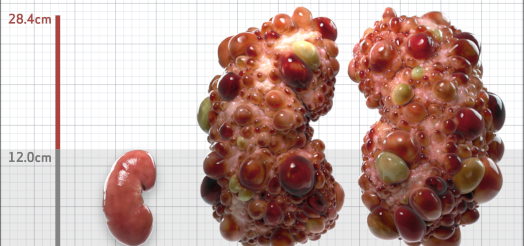
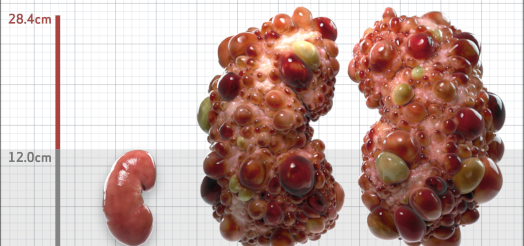
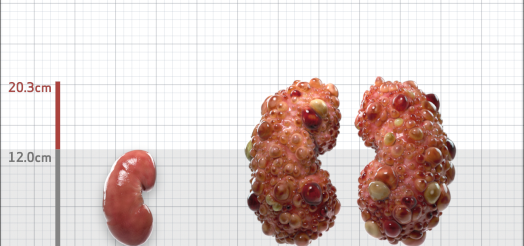
| Kidney Size (mL/m) | 1343 | 150-250 |
- ADPKD Imaging Classification
ESTIMATED AGE AT KIDNEY FAILURE51
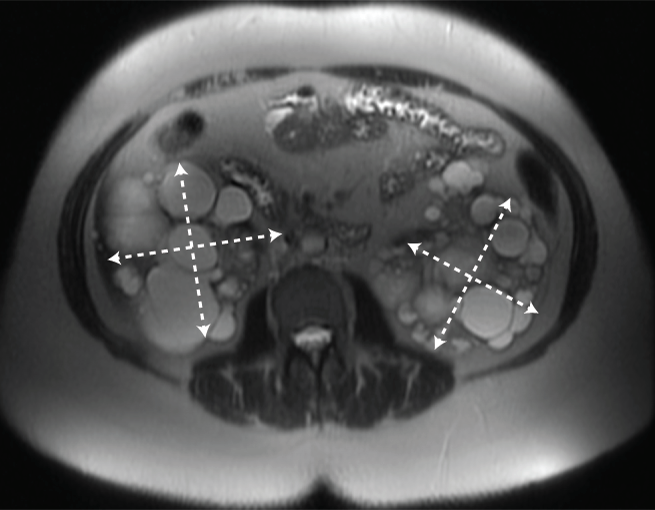
MRI/CT SCANS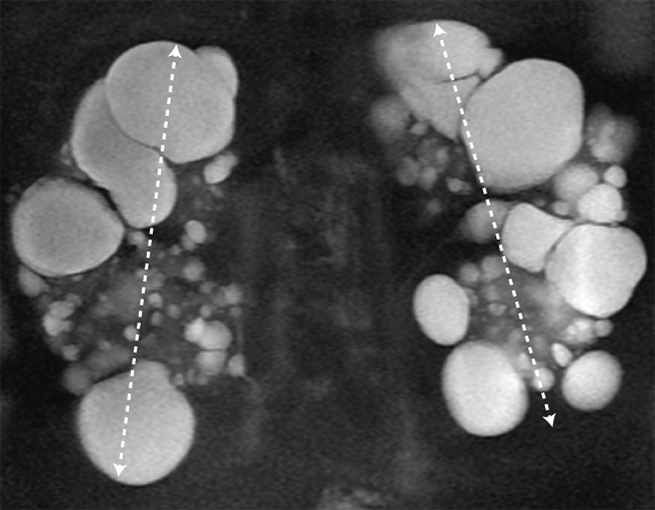
Disease Progression3-5

Click on the flags below to see the testing used to confirm risk of rapid disease progression as well as Marcus’ individual risk
Schrier RW, et al. Predictors of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease progression. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014;25:2399-2418.
Gansevoort RT, et al. Recommendations for the use of tolvaptan in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: a position statement on behalf of the ERA-EDTA Working Groups on Inherited Kidney Disorders and European Renal Best Practice. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2016;31(3):337-48.
Delgado, C. et al. (2022) “A unifying approach for GFR estimation: Recommendations of the NKF-ASN task force on reassessing the inclusion of race in diagnosing kidney disease,” American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 79(2). Available at: https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2021.08.003.
Irazabal MV, et al. Imaging classification of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: a simple model for selecting patients for clinical trials. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015;26:160-172.
Imaging classification of ADPKD: a simple model for selecting patients for clinical trials. http://www.mayo.edu/research/documents/pkd-center-adpkd-classification/doc-20094754. Accessed 1/11/2023.